PAROMOMYCIN SULFATE- paromomycin sulfate capsule, gelatin coated
X-GEN Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
----------
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules, USP, and other antibacterial drugs, Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules, USP should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
DESCRIPTION
Paromomycin sulfate is a broad spectrum antibiotic produced by Streptomyces riomosus var. paromomycinus. It is a white, amorphous, stable, water-soluble product. Paromomycin sulfate is designated chemically as 0-2, 6-Diamino-2, 6-dideoxy-β-L-idopyranosyl-(1→3)-0-β-D-ribofuranosyl-(1→5)-0-[2-amino-2-deoxy-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)]-2-deoxystreptamine sulfate (salt). The molecular formula is C23H45N5O14•xH2SO4, with a molecular weight of 615.64 (base). Its structural formula is:
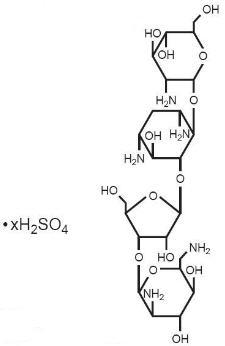
structure
Each capsule, for oral administration, contains paromomycin sulfate equivalent to 250mg paromomycin. Each capsule also contains the following inactive ingredients: Dark Blue Opaque (FD&C Blue 1, D&C Red 28, FD&C Red 40), Yellow Opaque (D&C Yellow 10), and titanium dioxide, USP.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The in-vitro and in-vivo antibacterial action of paromomycin closely parallels that of neomycin. It is poorly absorbed after oral administration, with almost 100% of the drug recoverable in the stool.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Paromomycin sulfate is indicated for intestinal amebiasis–acute and chronic (NOTE—It is not effective in extraintestinal amebiasis); management of hepatic coma–as adjunctive therapy.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules and other antibacterial drugs, Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Paromomycin sulfate is contraindicated in individuals with a history of previous hypersensitivity reactions to it. It is also contraindicated in intestinal obstruction.
PRECAUTIONS
Prescribing Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
The use of this antibiotic, as with other antibiotics, may result in an overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. Constant observation of the patient is essential. If new infections caused by nonsusceptible organisms appear during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken. The drug should be used with caution in individuals with ulcerative lesions of the bowel to avoid renal toxicity though inadvertent absorption.
Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Nausea, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea have been reported in patients on doses over 3 g daily.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Intestinal amebiasis: Adults and Pediatric Patients: Usual dose—25 to 35 mg/kg body weight daily, administered in three doses with meals, for five to ten days.
Management of hepatic coma: Adults: Usual dose—4 g daily in divided doses, given at regular intervals for five to six days.
HOW SUPPLIED
Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules, USP each contain paromomycin sulfate equivalent to 250 mg paromomycin, are supplied as follows:
NDC 39822-3250-1: Bottles of 100
The capsule is Dark Blue Opaque / Yellow Opaque, imprinted with “Ptek” in black ink on the cap and “817” with black ink on the body.
| PAROMOMYCIN SULFATE
paromomycin sulfate capsule, gelatin coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - X-GEN Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (790169531) |
