PROIN 25
-
phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride tablet, chewable
Pegasus Laboratories, Inc.
----------
Description:
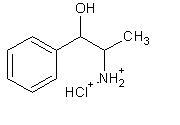
Description: PROIN (phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride) is a sympathomimetic amine closely related to ephedrine.Phenypropanolamine hydrochloride (PPA) is the nonpropietary designation for benzenemethanol,α - (1-aminoethyl) - hydrochloride, (R*,S*) - , (± ).
The empirical formula is C9H13NO• HCl and the molecular weight is 187.67. It is a white crystalline compound having a slight aromatic odor.
PPA is freely soluble in water and alcohol but is pratically insoluble in ether, benzene and chloroform. The chemical structure of phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride is:
Indication:
PROIN is indicated for the control of urinary incontinence due to urethral sphincter hypotonus in dogsDosage and Administration:
The total recommended dosage for oral oral administration is 2mg/kg (0.91mg/lb) for bodyweight twice daily. PROIN is scored and dosage should be calculated in half-tablet increments.
Caution:
For oral use in dogs onlyCaution: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Warnings:
Not for human use. Keep out of reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental accidental ingestion by humans.Precautions:
Precautions:
PROIN may cause increased thirst; therefore, provide ample fresh water. PROIN should be stored out of reach of dogs in a secured area.
Use in dogs with incontinence due to a urinary tract infection will mask symptoms. PROIN is not effective in dogs with incontinence due to neurologic disease or malformation.
PROIN may cause hypertension; therefore, use with caution in dogs with pre-existing heart disease, hypertension, liver disease, kidney insufficiency, diabetes, glaucoma, and conditions a predilection for hypertension. Use with caution in dogs receiving sympathomimetic drugs, tricyclic antidepressants, or monoamine oxidase inhibitors as increased toxicity may result. Use with caution in dogs administered halogenated gaseous anesthetics as this may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias.
A laboratory study on human blood revealed that PPA used in conjunction with aspirin may potentiate decreased platelet aggregation.
The safe use of PROIN in dogs used for breeding purposes, during pregnancy or in lactating bitches has not been evaluated.
Adverse Reactions:
Adverse Reaction:
A placebo controlled clinical study involving 123 PROIN treated dogs and 61 placebo treated dogs was conducted for 28 days. The most common adverse reactions are shown in Table 1 below. In addition, one dog exhibited disorientation, nervousness, a 7.7% loss of body weight, and hypertension with proteinuria. A second dog exhibited restless behavior, lethargy, a 2.8% body weight loss and proteinuria.
Table 1: Number and percentage of dogs with adverse reactions in the 28 day placebo-controlled clinical study| Adverse Reactions | PROIN Treated (N=123) | Placebo Treated (N=61) |
| Emesis | 20.3% | 8.2% |
| Hypertension (≥ 160mm Hg)1 | 19.5% | 14.7% |
| Anorexia | 16.3% | 3.3% |
| Body weight loss (> 5%) 2
| 16.1% | 6.8% |
| Proteinuria | 13.0% | 8.2% |
| Anxiety/aggression/behavior change | 9.7% | 3.2% |
| Diarrhea | 7.3% | 9.8% |
| Polydipsia | 6.5% | 9.8% |
| Lethargy | 5.7% | 1.6% |
| Musculoskeletal Disorder | 3.2% | 1.6% |
| Insomnia/Sleep Disorder | 2.5% | 0.0% |
1 One or more systolic blood pressure reading of ≥ 160mmHg.
2 The "N" for weight loss is PROIN treated N=118 and placebo N=59 because seven dogs did not have a final weight at the time of withdrawal from the study.
One hundred and fifty seven dogs continued into the 6 month open label clinical study the most common adverse reactions are listed in Table 2. In addition, one dog exhibited progressively worsening hypertension with proteinuria. Five dogs enrolled in the study with pre-existing heart disease. Of these, one dog developed systolic failure with an unknown reaction to treatment.
Table 2: Number and percentage of dogs with adverse reactions in the 6 month open label clinical study.
| Adverse Reactions | Total N= 125 |
| Hypertension (>160 mmHg) 1 | 34.5% |
| Body Weight Loss (> 5%) | 24.8% |
| Emesis | 19.7% |
| Proteinuria | 15.3% |
| Anorexia | 10.2% |
| Diarrhea | 6.4% |
| Lethargy | 5.7% |
| Anxiety/ behavior change/ aggression | 5.7% |
Reports of death in dogs treated with phenylpropanolamine have been received by the FDA Center for Veterinary Medicine. Vocalization, neurologic signs and collapse were also reported in some of these cases. A necropsy of one of dog revealed subarachroidal and intraventricular hemorrhage in the brain.
For a copy of the Material Safety and Data Sheet (MSDS) or to report adverse reactions, call Pegasus Laboratories at 1-800-874-9764.
Information for Owner or Person Treating Animal:
Always follow the dosage instructions for PROIN provided by your veterinarian. Monitor your dog after giving PROIN to be sure all of it is consumed. If you have difficulty giving PROIN contact your veterinarian.
It may take several days of treatment with PROIN before urinary incontinence improves. If you miss a dose, give it as soon as you remember. If it is close to the next dose, skip the dose you missed and go back to the regular dosing schedule. Do not give two doses at once. PROIN should only be given to the dog for which it was prescribed. Because PROIN is flavored, store it in a secure area.
Contact your veterinarian if you notice restlessness or irritability, loss of appetite, the incontinence persists or worsens, or any other unusual signs.
Consult your veterinarian before using PROIN with any other medications.
Clinical Pharmacology:
Phenylpropanolamine is a chemical analogue of the endogenous sympathomimetic amines. It is an alpha-adrenergic agent which has been reported to increase urethral tone in dogs 2. Its mechanism of action is not well determined, but it is believed to cause the release of norepinephrine by indirectly stimulating both the alpha and beta-adrenergic receptors of the smooth muscle to increase smooth muscle tone of the urethra, bladder neck, and the internal urethral sphincter 3, 4.
The pharmacokinetics of phenylpropanolamine in dogs has not been well studied. In humans, phenylpropanolamine is readily absorbed after oral administration of solid dosage forms and has an onset of action of approximately 15-30 minutes and duration of effect of about three hours. In a published study in dogs, phenylpropanolamine disposition was characterized in three dogs administered phenylpropanolamine intravenously and orally in immediate release and controlled release formulations 5. The terminal elimination half-life averaged 3.5 ± 0.5 hours after the intravenous dose. Oral absorption from the immediate release capsule was rapid and bioavailability was 98.2 ± 6.9 percent. Absorption of phenylpropanolamine from the controlled release dosage form was biphasic; an initial rapid phase was followed by second slower absorption phase which continued over 16 hours. Plasma concentrations then declined with a half-life roughly parallel to the intravenous and oral immediate release half-lives. Oral bioavailability from the controlled release tablet was 93.7 ± 5.9 percent.
Effectiveness:
A 28 day placebo-controlled clinical study was conducted in 21 study sites across the U.S. The study included 184 dogs with urinary incontinence due to sphincter hypotonus of which 127 dogs (100 female, 27 male) were evaluated for effectiveness. Dogs were randomly assigned either to receive 2mg/kg PROIN (123 dogs) or placebo (61 dogs) administered twice daily for 28 days. PROIN was effective in controlling urinary incontinence based on decrease in urinary accidents per week. Changes to hematology and serum chemistry were not considered clinically significant or related to treatment.
Table 3: Mean urinary accidents per week by treatment group, females
| Week | Mean Urinary Accidents (PROIN-treated, N=66) | Mean Urinary Accidents (Placebo-treated, N=34) |
| Pretreatment | 9.0 | 7.8 |
| 1 | 3.9 | 4.8 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 4.1 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 3.1 |
| 4 | 1.6 | 2.8 |
The dogs voluntarily consumed 53.9% of the doses and 33.7% of the doses in food. The owners pilled the dogs 12.1% of the doses and were unable to administer 0.3% of the doses.
Animal Safety Studies:
Effectiveness:
In a target animal safety study, PROIN was administered to 32 healthy male and female Beagle dogs at 0, 2 6 and 10 mg/kg of body weight (0, 3, and five times the recommended dose: 8 dogs per group) twice daily for 26 consecutive weeks. The most pronounced finding was a dose dependent increase increase in the blood pressure. Mean systolic blood pressure was increased in all PPA-treated groups compared to the control, but mean values for all 4 groups were within the normal range. Mean diastolic and mean MAP (mean arterial pressure) were higher in the 3X and 5X groups and in the 1X males. Dogs in the 3X and 5X groups had more individual systolic , diastolic, and MAP values above the normal range than the control group dogs. A dose dependent decrease in heart rate was observed in the 3X and 5X dogs. In the 0, 1, 3, and 5X groups, 5%, 34%, 44% and 40% of the total number of heart rates obtained from electrocardiograms for each group over the course of the study were below the normal range (70-120 beats per minute) with the lowest value being 51 bpm in 4of the 1X group dogs. One dog in each of the 1X and 5X had an elevated heart rate between 150-180 beats per minute on at least 2 of the 13 physical exams. One dog in each in each of the 1X and 3X groups developed gallop heart sounds after treatment began that were noted in 12 of 13 and 6 of 13 physical exams respectively. Dogs in the PPA-treated group exhibited anxious/ restless behavior more frequently than the mean controlled group. One dog each in the 1X and 3X were responsible for the majority f the observations. A decline in mean body weight and body condition was observed in females in all 4 groups, including the control. One female in the 1Xgroup lost 33% body weight. Vomiting and loose stool occurred in a dose related fashion, and most of the vomiting episodes took place within1 hour of dosing. Mean platelet counts were higher in at least one of the PPA treated groups. With individual vales up to 1.4X the upper limit of normal (ULN) in the 3X and 5X group. The 3X and 5X groups had higher mean serum ALT values compared to the control. Mean ALT was within the normal range for all 4 groups. There were more dogs with ALT levels above the normal range in the 3X PPA treated compared to the control., but increased values were transient and less than 1.8X ULN. All dogs had ALN values in the normal range at the conclusion of the study.
In a separate tolerance study, 6 healthy female Beagle dogs were administered PROIN at 20mg/kg body weight (10 times the recommended dose) twice daily for 21 consecutive days. Mean systolic blood pressure was increased in the 10X group compared to the control, but mean values were within the normal range for both groups. Mean diastolic pressures were above the normal range on days 7 and 21 for the !0X group, and day 14 for the control. The 10X dogs had hypertensive MAP values on day s 7 and 21, whereas, the control dog mean MAP values were in the normal range. There was a trend in the 10X dogs for lower heart rates following initiation of PPA treatment. Four of 6 dogs in the 10X group had heart rates below the normal range on day 7, whereas none of the control dogs did. The 10X group dogs had increased hematocrit, hemoglobin, RBC counts, urine specific gravity, and water intake consistent with transient sub-clinical dehydration that occurred shortly after PPA treatment was started. All six dogs in the 10X group vomited at least once during the treatment period, whereas only 1 of the control dogs did. Most of the vomiting episodes took place within 1 hour of dosing. Mean platelet counts were also higher in the 10X dogs on all 3 exam days, mean values were above the normal range on day 7, with individual values up to 1.5X ULN. The 10X group had a higher mean serum ALT value on day 7 than the control. Mean ALT values for both groups were in the normal range on all 3 exam days, but 2 dogs in the 10X group had ALT vlaues up to 1.4XULNon day 7; these elevated values were transient, and all dogs had ALN values in the normal range on days 14 and 21.
For either study, there was no evidence of chronic hypertension-induced target organ damage, there were no clinical findings attributed to PPA on the ophthalmic exams, electrocardiogram evaluation, or gross necropsy and histopathology.
Storage:
Store at controlled room temperature 20-25°C (68-77°F) excursions permitted between (15-40°C (59-104 °F)
How Supplied:
PROIN is scored and contain 25, 50 or 75mg phenylpropanolamine (as hydrochloride) per tablet. Twenty five and 50mg tablets are packaged in bottles containing 60 or 180 tablets, and the 75mg tablets are packaged in bottles containing 60 tablets.
NADA#141-324. Approved by the FDA
PROIN ® is a registered trademark of Pegasus Laboratories, Inc.
References:
1 Watson R, et. al. Ephedra alkaloids inhibit platelet aggregation. Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolysis. 2010 21: 266-271
2 Richter K. P., Ling G.V. Clinical response and urethral pressure profile changes after phenylpropanolamine in dogs with primary sphincter incompetence. JAVMA Vol 187 No. 6, September 15, 1985 605-611.
3 Scott L., Leddy M., and Bernay F. Evaluation of phenylpropanolamine in the treatment of urethral sphincter mechanism incompetence in the bitch. J. Small Animal Pract.2002, 43 (11)493-6.
4 Noel S., et. al. Combined pharmacokinetic and urodynamic study of the effects of oral administration of phenylpropanolamine in female Beagle dogs. Vet Journal, 2010. 184 (2): 201-207.
5 Hussain M.A,, Aungst B.J., Lam G., and Shefter E. Phenylpropanolamine pharmacokinetics in dogs after intravenous, oral and controlled release doses. Biopharm Drug Dispos, Vol 8 No. 5. September 1987. 497-505.
Warnings:
Warning: Keep out of reach of children. Not for human use. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans. For use in dogs only.
Precautions: PROIN Chewable tablets should be stored out of reach of dogs in a secured area. To report adverse reactions call Pegasus Laboratories 1800-874-9764.
Please refer to attached label for complete Warnings and Precautions.
Store at controlled room temperature 20-25°C (68-77°F) excursions permitted between (15-40°C (59-104 °F)
Principle Display Panel:
NDC #49427-315-48 or NDC #49427-315-50
PROIN 25mg
(phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride)
Chewable Tablets
25mg per Tablet
For oral use in dogs only
60 or 180 Tablets
Caution: Federal law restricts this drug to us by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Sympathomimetic amine drug.
NADA # 141- 324
PRN Pharmacal Pegasus Laboratories, Inc.
Manufactured by:
Pegasus Laboratories Inc.
An Employee-Owned Company
Pensacola, FL 32514, USA
| PROIN 25
phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride tablet, chewable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Marketing Information | |||
| Marketing Category | Application Number or Monograph Citation | Marketing Start Date | Marketing End Date |
| NADA | NADA141324 | 09/01/2001 | |
| Labeler - Pegasus Laboratories, Inc. (108454760) |
| Registrant - Pegasus Laboratories, Inc. (108454760) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Operations |
| Pegasus Laboratories, Inc. | 108454760 | manufacture, analysis | |
Revised: 09/2011 Pegasus Laboratories, Inc.