ADREVIEW- iobenguane i-123 injection
Medi-Physics Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use AdreView safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AdreView.
AdreView (Iobenguane I 123 Injection) for Intravenous Use Initial U.S. Approval: 2008 INDICATIONS AND USAGEAdreView is a diagnostic radiopharmaceutical agent for gamma-scintigraphy. It is indicated for use in the detection of primary or metastatic pheochromocytoma or neuroblastoma as an adjunct to other diagnostic tests. (1) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS5 mL of sterile solution for intravenous injection in a single use vial (2 mCi/mL at calibration time). (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSKnown hypersensitivity to iobenguane or iobenguane sulfate. (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSSerious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported following AdreView administration. The most common adverse reactions, dizziness, rash, pruritis, flushing and injection site hemorrhage occurred in < 1% of patients. (6.1, 6.2) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GE Healthcare at 1-800-654-0118 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONSAmitryptiline and derivatives, imipramine and derivatives, other antidepressants that inhibit norepinephrine transporter, antihypertensives that deplete norepinephrine stores or inhibit reuptake, sympathomimetric amines and cocaine: Discontinue for 5 biological half-lives prior to AdreView administration. (7) USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 10/2012 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AdreView is a radiopharmaceutical indicated for use in the detection of primary or metastatic pheochromocytoma or neuroblastoma as an adjunct to other diagnostic tests.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Radiation Safety
AdreView emits radiation and must be handled with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure to clinical personnel and patients. Radiopharmaceuticals should be used by or under the control of physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate government agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides. AdreView dosing is based upon the radioactivity determined using a suitable calibration system immediately prior to administration.
To minimize radiation dose to the bladder, prior to and following AdreView administration, encourage hydration to permit frequent voiding. Encourage the patient to void frequently for the first 48 hours following AdreView administration [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
2.2 Thyroid Blockade
Before administration of AdreView, administer Potassium Iodide Oral Solution or Lugol's Solution (equivalent to 100 mg iodide for adults, body-weight adjusted for children) or potassium perchlorate (400 mg for adults, body-weight adjusted for children) to block uptake of iodine 123 by the patient's thyroid. Administer the blocking agent at least one hour before the dose of AdreView [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.3 Preparation and Administration
Inspect the AdreView vial for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Use aseptic procedures and a radiation shielding syringe during administration. Administer the dose as an intravenous injection over 1 to 2 minutes. A subsequent injection of 0.9% sodium chloride may be used to ensure full delivery of the dose.
2.4 Recommended Dose for Adults
For adults (≥ 16 years of age), the recommended dose is 10 mCi (370 MBq) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
2.5 Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients
For pediatric patients < 16 years of age weighing ≥ 70 kg, the recommended dose is 10 mCi (370 MBq) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
For pediatric patients < 16 years of age weighing < 70 kg, the recommended dose should be calculated according to patient body weight as shown in Table 1 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The benzyl alcohol in AdreView may cause serious adverse reactions in premature or low birth-weight infants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
| Weight (kg) | Fraction of adult activity | AdreView (mCi) pediatric dose | AdreView (MBq) pediatric dose |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| 3 | 0.1 | 1 | 37 |
| 4 | 0.14 | 1.4 | 52 |
| 6 | 0.19 | 1.9 | 70 |
| 8 | 0.23 | 2.3 | 85.1 |
| 10 | 0.27 | 2.7 | 99.9 |
| 12 | 0.32 | 3.2 | 118.4 |
| 14 | 0.36 | 3.6 | 133.2 |
| 16 | 0.4 | 4 | 148 |
| 18 | 0.44 | 4.4 | 162.8 |
| 20 | 0.46 | 4.6 | 170.2 |
| 22 | 0.5 | 5 | 185 |
| 24 | 0.53 | 5.3 | 196.1 |
| 26 | 0.56 | 5.6 | 207.2 |
| 28 | 0.58 | 5.8 | 214.6 |
| 30 | 0.62 | 6.2 | 229.4 |
| 32 | 0.65 | 6.5 | 240.5 |
| 34 | 0.68 | 6.8 | 251.6 |
| 36 | 0.71 | 7.1 | 262.7 |
| 38 | 0.73 | 7.3 | 270.1 |
| 40 | 0.76 | 7.6 | 281.2 |
| 42 | 0.78 | 7.8 | 288.6 |
| 44 | 0.8 | 8 | 296 |
| 46 | 0.82 | 8.2 | 303.4 |
| 48 | 0.85 | 8.5 | 314.5 |
| 50 | 0.88 | 8.8 | 325.6 |
| 52 | 0.9 | 9 | 333 |
| 54 | 0.9 | 9 | 333 |
| 56 | 0.92 | 9.2 | 340.4 |
| 58 | 0.92 | 9.2 | 340.4 |
| 60 | 0.96 | 9.6 | 355.2 |
| 62 | 0.96 | 9.6 | 355.2 |
| 64 | 0.98 | 9.8 | 362.6 |
| 66 | 0.98 | 9.8 | 362.6 |
| 68 | 0.99 | 9.9 | 366.3 |
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
The estimated absorbed radiation doses to adults and children from intravenous administration of AdreView are as shown in Table 2:
| ABSORBED DOSE PER UNIT ADMINISTERED ACTIVITY | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORGAN / TISSUE | ADULT | 15-YEAR OLD | 10-YEAR OLD | 5-YEAR OLD | 1-YEAR OLD | NEONATES | |||||||
| µGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | µGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | µGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | µGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | µGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | µGy/ MBq | rad/mCi | ||
| *OLINDA/EXM calculation based on biodistribution data from Swanson et al. and Publication 53 of the ICRP (International Commission on Radiological Protection) [Annals of the ICRP 1987; 18 (1-4): 329-331] | |||||||||||||
| Adrenals | 16 | 0.059 | 21 | 0.078 | 31 | 0.115 | 42 | 0.155 | 67 | 0.248 | 111 | 0.411 | |
| Brain | 3.9 | 0.014 | 4.9 | 0.018 | 8.1 | 0.030 | 13 | 0.048 | 24 | 0.089 | 55.9 | 0.207 | |
| Breast | 4.7 | 0.017 | 5.9 | 0.022 | 9.4 | 0.035 | 15 | 0.056 | 28 | 0.104 | 65.3 | 0.242 | |
| Gallbladder | 20 | 0.074 | 24 | 0.089 | 34 | 0.126 | 51 | 0.189 | 95 | 0.352 | 200 | 0.740 | |
| GI Tract | Stomach Wall | 7.6 | 0.028 | 10 | 0.037 | 17 | 0.063 | 27 | 0.100 | 51 | 0.189 | 114 | 0.422 |
| Small Intestine Wall | 7.7 | 0.028 | 9.8 | 0.036 | 16 | 0.059 | 25 | 0.093 | 46 | 0.170 | 104 | 0.385 | |
| Colon Wall | 8.1 | 0.030 | 10 | 0.037 | 16 | 0.059 | 26 | 0.096 | 46 | 0.170 | 104.3 | 0.386 | |
| Upper Large Intestine Wall | 8.4 | 0.031 | 11 | 0.041 | 18 | 0.067 | 30 | 0.111 | 53 | 0.196 | 119 | 0.440 | |
| Lower Large Intestine Wall | 7.7 | 0.028 | 9.6 | 0.036 | 15 | 0.056 | 21 | 0.078 | 38 | 0.141 | 84.9 | 0.314 | |
| Heart Wall | 18 | 0.067 | 23 | 0.085 | 35 | 0.130 | 53 | 0.196 | 94 | 0.348 | 182 | 0.673 | |
| Kidneys | 13 | 0.048 | 16 | 0.059 | 24 | 0.089 | 35 | 0.130 | 59 | 0.218 | 132 | 0.488 | |
| Liver | 67 | 0.248 | 87 | 0.322 | 130 | 0.481 | 180 | 0.666 | 330 | 1.221 | 720 | 2.664 | |
| Lungs | 16 | 0.059 | 23 | 0.085 | 32 | 0.118 | 48 | 0.178 | 89 | 0.329 | 215 | 0.796 | |
| Muscles | 6 | 0.022 | 7.6 | 0.028 | 12 | 0.044 | 17 | 0.063 | 33 | 0.122 | 75.1 | 0.278 | |
| Esophagus | 6 | 0.022 | 7.6 | 0.028 | 11 | 0.041 | 18 | 0.067 | 32 | 0.118 | 72.2 | 0.267 | |
| Osteogenic Cells | 16 | 0.059 | 21 | 0.078 | 31 | 0.115 | 47 | 0.174 | 100 | 0.370 | 254 | 0.940 | |
| Ovaries | 7.9 | 0.029 | 10 | 0.037 | 15 | 0.056 | 22 | 0.081 | 41 | 0.152 | 92.3 | 0.342 | |
| Pancreas | 12 | 0.044 | 15 | 0.056 | 25 | 0.093 | 39 | 0.144 | 68 | 0.252 | 143 | 0.529 | |
| Red marrow | 5.6 | 0.021 | 6.8 | 0.025 | 10 | 0.037 | 15 | 0.056 | 30 | 0.111 | 89.5 | 0.331 | |
| Skin | 3.7 | 0.014 | 4.4 | 0.016 | 7.1 | 0.026 | 11 | 0.041 | 21 | 0.078 | 53.1 | 0.196 | |
| Spleen | 20 | 0.074 | 27 | 0.100 | 42 | 0.155 | 64 | 0.237 | 110 | 0.407 | 282 | 1.043 | |
| Testes | 5.4 | 0.020 | 7.1 | 0.026 | 11 | 0.041 | 16 | 0.059 | 30 | 0.111 | 69.9 | 0.259 | |
| Thymus | 6 | 0.022 | 7.6 | 0.028 | 11 | 0.041 | 18 | 0.067 | 32 | 0.118 | 72.2 | 0.267 | |
| Thyroid | 4.7 | 0.017 | 6.1 | 0.023 | 9.9 | 0.037 | 16 | 0.059 | 30 | 0.111 | 69.4 | 0.257 | |
| Urinary Bladder Wall | 66 | 0.244 | 84 | 0.311 | 110 | 0.407 | 110 | 0.407 | 200 | 0.740 | 478.0 | 1.769 | |
| Uterus | 11 | 0.041 | 14 | 0.052 | 21 | 0.078 | 28 | 0.104 | 51 | 0.189 | 110.0 | 0.407 | |
| Whole Body | 8.1 | 0.030 | 10 | 0.037 | 16 | 0.059 | 24 | 0.089 | 44 | 0.163 | 104.0 | 0.385 | |
| EFFECTIVE DOSE | µSv/MBq | 13.7 | 18.1 | 26.7 | 37.6 | 68 | 162 | ||||||
| mSv/mCi | 0.507 | 0.670 | 0.988 | 1.39 | 2.52 | 6 | |||||||
The effective dose resulting from an administered activity amount of 10 mCi is 5.07 mSv in an adult.
2.7 Imaging Guidelines
Begin whole body planar scintigraphy imaging 24 ± 6 hours following administration of AdreView. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) may be performed following planar scintigraphy, as appropriate [see Clinical studies 14.1].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Single use vials containing 5 mL solution for intravenous injection (2 mCi/mL at calibration time).
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
AdreView is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to iobenguane or iobenguane sulfate.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported following AdreView administration. Prior to administration, question the patient for a history of prior reactions to iodine, an iodine-containing contrast agent or other products containing iodine. If the patient is known or strongly suspected to have hypersensitivity to iodine, an iodine-containing contrast agent or other products containing iodine, the decision to administer AdreView should be based upon an assessment of the expected benefits compared to the potential hypersensitivity risks. Have anaphylactic and hypersensitivity treatment measures available prior to AdreView administration [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.2 Risks for Benzyl Alcohol Toxicity in Infants
AdreView contains benzyl alcohol at a concentration of 10.3 mg/mL. Benzyl alcohol has been associated with a fatal "Gasping Syndrome" in premature infants and infants of low birth weight. Exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol has been associated with toxicity (hypotension, metabolic acidosis), particularly in neonates, and an increased incidence of kernicterus, particularly in small preterm infants. There have been rare reports of deaths, primarily in preterm infants, associated with exposure to excessive amounts of benzyl alcohol [see Description (11)].
Observe infants for signs or symptoms of benzyl alcohol toxicity following AdreView administration. AdreView safety and effectiveness have not been established in neonates (pediatric patients below the age of 1 month).
5.3 Increased Radiation Exposure in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
AdreView is cleared by glomerular filtration and is not dialyzable. The radiation dose to patients with severe renal impairment may be increased due to the delayed elimination of the drug. Delayed AdreView clearance may also reduce the target to background ratios and decrease the quality of scintigraphic images. These risks importantly may limit the role of AdreView in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with severe renal impairment. AdreView safety and efficacy have not been established in these patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.4 Thyroid Accumulation
Failure to block thyroid uptake of iodine 123 may result in an increased long term risk for thyroid neoplasia. Administer thyroid blocking medications before AdreView administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.5 Risks with Concomitant Medication Withdrawal
Drugs which interfere with norepinephrine uptake or retention may decrease the uptake of AdreView in neuroendocrine tumors and lead to false negative imaging results. When medically feasible, stop these drugs before AdreView administration and monitor patients for the occurrence of clinically significant withdrawal symptoms, especially patients with elevated levels of circulating catecholamines and their metabolites [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.6 Hypertension
Assess the patient's pulse and blood pressure before and intermittently for 30 minutes after AdreView administration. AdreView may increase release of norepinephrine from chromaffin granules and produce a transient episode of hypertension, although this was not observed in the clinical study. Prior to AdreView administration, ensure emergency cardiac and anti-hypertensive treatments are readily available.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Study Experience
Serious adverse reactions were not observed in the AdreView clinical study. The data described below reflect AdreView exposure to 251 patients with known or suspected pheochromocytoma or neuroblastoma. The average ages were 49 years (range 17 - 88 years) for adults and, for pediatric patients, 4 years (range 1 month - 16 years). Slightly less than half the patients were male. All patients were monitored for adverse reactions over a 24 hour period following AdreView administration.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions were all mild to moderate in severity and were predominantly isolated occurrences (≤ 2 patients) of one of the following reactions: dizziness, rash, pruritus, flushing or injection site hemorrhage.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because postmarketing reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity reactions have uncommonly been reported during the postmarketing use of AdreView [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The following drugs have the potential to decrease the uptake of norepinephrine and cause false negative imaging results: antihypertensives that deplete norepinephrine stores or inhibit reuptake (e.g., reserpine, labetalol), antidepressants that inhibit norepinephrine transporter function (e.g., amitriptyline and derivatives, imipramine and derivatives, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), sympathomimetic amines (e.g., phenylephrine, phenylpropanolamine, pseudoephedrine and ephedrine), and cocaine. Clinical studies have not determined which specific drugs may cause false negative imaging results nor whether all drugs in any specific pharmacologic class have the same potential to produce the negative imaging results. Increasing the dose of AdreView will not overcome any potential uptake limiting effect of these drugs. Before AdreView administration, discontinue (for at least 5 biological half-lives) drugs known or expected to reduce norepinephrine uptake, as clinically tolerated.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C: Any radiopharmaceutical, including AdreView, has a potential to cause fetal harm. It is not known whether AdreView can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with AdreView. AdreView should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether AdreView is excreted into human milk. However, iodine 123 is excreted into human milk. Because many drugs are excreted into human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to interrupt nursing after administration of AdreView or not to administer AdreView, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother. Based on the physical half-life of iodine 123 (13.2 hours) nursing women may consider interrupting nursing for 6 days after AdreView administration in order to minimize risks to nursing infants.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of AdreView have been established in the age groups 1 month to 16 years [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 1 month have not been established [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
The AdreView clinical study did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly population should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
AdreView is excreted by the kidneys, and the risks of adverse reactions, increased radiation dose, and occurrence of falsely negative imaging results may be greater in patients with severely impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection and image interpretation. Consider assessment of renal function in elderly patients prior to AdreView administration.
10 OVERDOSAGE
The major manifestations of overdose relate predominantly to increased radiation exposure, with the long term risks for neoplasia.
11 DESCRIPTION
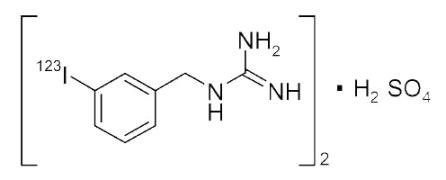
AdreView (Iobenguane I 123 Injection) is a sterile, pyrogen-free radiopharmaceutical for intravenous injection. Each mL contains 0.08 mg iobenguane sulfate, 74 MBq (2 mCi) of I 123 (as iobenguane sulfate I 123) at calibration date and time on the label, 23 mg sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, 2.8 mg disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate and 10.3 mg (1% v/v) benzyl alcohol with a pH of 5.0 – 6.5. Iobenguane sulfate I 123 is also known as I 123 meta-iodobenzlyguanidine sulfate and has the following structural formula:
11.1 Physical Characteristics
Iodine 123 is a cyclotron-produced radionuclide that decays to Te 123 by electron capture and has a physical half-life of 13.2 hours.
| Radiation | Energy Level (keV) | Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 159 | 83 |
11.2 External Radiation
The specific gamma ray constant for iodine 123 is 1.6 R/mCi-hr at 1 cm. The first half value thickness of lead (Pb) for I 123 is 0.04 cm. The relative transmission of radiation emitted by the radionuclide that results from interposition of various thicknesses of Pb is shown in Table 4 (e.g., the use of 2.16 cm Pb will decrease the external radiation exposure by a factor of about 1,000).
| Shield Thickness cm of lead (Pb) | Reduction in In-air Collision Kerma |
|---|---|
|
|
| 0.04 | 0.5 |
| 0.13 | 10-1 |
| 0.77 | 10-2 |
| 2.16 | 10-3 |
| 3.67 | 10-4 |
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Iobenguane is similar in structure to the antihypertensive drug guanethedine and to the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (NE). Iobenguane is, therefore, largely subject to the same uptake and accumulation pathways as NE. Iobenguane is taken up by the NE transporter in adrenergic nerve terminals and stored in the presynaptic storage vesicles. Iobenguane accumulates in adrenergically innervated tissues such as the adrenal medulla, salivary glands, heart, liver, spleen and lungs as well as tumors derived from the neural crest. By labeling iobenguane with the isotope iodine 123, it is possible to obtain scintigraphic images of the organs and tissues in which the radiopharmaceutical accumulates.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
AdreView is a diagnostic radiopharmaceutical which contains a small quantity of iobenguane that is not expected to produce a pharmacodynamic effect [see Description (11)]. To minimize radiation dose to the thyroid gland, this organ should be blocked before dosing [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Since iobenguane is excreted mainly via the kidneys, patients with severe renal insufficiency may experience increased radiation exposure and impaired imaging results. Frequent voiding should be encouraged after administration to minimize the radiation dose to the bladder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. The calculation of the estimated radiation dose is shown in Table 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Iobenguane is rapidly cleared from the blood and accumulates in adrenergically innervated tissues [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. Retention is especially prolonged in highly adrenergically innervated tissues (e.g., the adrenal medulla, heart, and salivary glands).
The majority of the iobenguane dose is excreted unaltered by the kidneys via glomerular filtration. A rapid initial clearance of circulating iobenguane is observed, followed by a slow clearance as iobenguane is released from other compartments. In patients with normal renal function, 70 to 90% of the administered dose is recovered unaltered in urine within 4 days. Iobenguane is not cleared by dialysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Most of the remaining radioactivity recovered in the urine is in the form of the radioiodinated metabolite m-iodohippuric acid (MIHA) (typically ≤ 10%) and free radioiodide (typically ≤ 6%). The enzymatic process responsible for metabolism has not been well characterized and the pharmacologic activity of these metabolites has not been studied. Only a small amount (< 1%) of the injected dose is eliminated via the feces.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Iobenguane hemisulfate was not mutagenic in vitro in the Ames bacterial mutation assay and in the in vitro mouse lymphoma test, and was negative in the in vivo micronucleus test in rats.
Long-term animal studies have not been conducted to evaluate AdreView's carcinogenic potential or potential effects on fertility.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Iobenguane sulfate testing in dogs revealed electrocardiographic (ECG) changes after administration of 202 times the mg/m2 conversion of the maximum human dose for a 60 kg adult; the no observable effect level (NOEL) was not determined. When iobenguane was tested in a cell system stably expressing hERG-1 potassium channels, inhibition of potassium channels was not observed at an 80 μM iobenguane concentration and the IC50 was 487 μM.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Pheochromocytomas and Neuroblastomas
The safety and efficacy of AdreView were assessed in an open-label, multicenter, multinational trial of 251 subjects with known or suspected neuroblastoma or pheochromocytoma. Diagnostic efficacy for the detection of metabolically active neuroblastoma or pheochromocytoma was determined by comparison of focal increased radionuclide uptake on planar scintigraphy at 24 ± 6 hours post-administration of AdreView against the definitive diagnosis (standard of truth). Anterior and posterior planar whole-body images, or alternatively whole-body overlapping spot images, were acquired from the head to below the knees. Additional spot images were performed as deemed appropriate at the discretion of the clinical image reviewer. SPECT imaging of the thorax and abdomen was then obtained when possible.
Of the 251 subjects dosed with AdreView, 100 had known or suspected neuroblastoma and 151 had known or suspected pheochromocytoma. The population included 154 adults and 97 pediatric patients; the majority of adults were female (59%), the majority of pediatric subjects were male (58%). The adult subjects had a mean age of 49 years (range 17 to 88 years). The pediatric patients (56 males and 41 females) consisted of 32 infants (1 month up to 2 years of age), 62 children (2 years up to 12 years) and three adolescents (12 years up to 16 years).
The definitive diagnosis (standard of truth) for the presence or absence of metabolically active pheochromocytoma or neuroblastoma was determined by histopathology or, when histopathology was unavailable, a composite of imaging (i.e., CT, MRI, [131I]-mIBG scintigraphy), plasma/urine catecholamine and/or catecholamine metabolite measurements, and clinical follow-up.
A standard of truth was available for 211 subjects (127 with pheochromocytoma, 84 with neuroblastoma) and this group comprised the diagnostic efficacy population. For 93 of these subjects, the standard of truth was based solely upon histopathology. Of 211 subjects in the efficacy population, all had planar scintigraphy and 167 subjects had SPECT in addition to planar imaging. All images were assessed independently by three readers blinded to all clinical data. Table 5 summarizes the AdreView performance characteristics, by reader.
| Outcome | Reader A | Reader B | Reader C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (n = 159) | |||
| Point estimate | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.79 |
| 95% confidence interval | 0.73 - 0.86 | 0.70 - 0.84 | 0.71 - 0.85 |
| Specificity (n = 52) | |||
| Point estimate | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.69 |
| 95% confidence interval | 0.63 - 0.87 | 0.59 - 0.84 | 0.55 - 0.81 |
Performance characteristics (sensitivity and specificity) of AdreView planar imaging in patients with known or suspected neuroblastoma were similar to those in patients with known or suspected pheochromocytoma. Among the selected patients who also underwent SPECT imaging, similar performance characteristics of AdreView scintigraphy were observed when SPECT plus planar imaging was compared to planar imaging alone.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
AdreView is supplied in 10 mL glass vials containing a total volume of 5 mL of solution with a total radioactivity of 370 MBq (10 mCi) at calibration time. Each vial is enclosed in a lead container of appropriate thickness.
NDC 17156-235-01
Storage
Store AdreView at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [see USP]. This product does not contain a preservative. Store within the original lead container or equivalent radiation shielding.
In accordance with USP recommendations Iobenguane I 123 Injection preparations should not be used after the expiration date and time stated on the label.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Instruct patients to inform their physician or healthcare provider if they:
- are pregnant or breast feeding.
- are sensitive to iodine, an iodine-containing contrast agent or other products that contain iodine.
- are sensitive to Potassium Iodide Oral Solution, or Lugol's Solution.
- have reduced renal function.
Instruct patients to increase their level of hydration prior to receiving AdreView and to void frequently for the first 48 hours following AdreView administration.
Manufactured and Distributed by
GE Healthcare, Medi-Physics, Inc.
Arlington Heights, IL 60004 U.S. A.
AdreView is a trademark of GE Healthcare.
GE and the GE Monogram are trademarks of
General Electric Company.
© 2011 General Electric Company – All rights reserved.
43-2035A
Revised May 2011
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mL Vial Label
GE Healthcare
AdreView™
Iobenguane I 123
Injection
Sterile, Pyrogen-free, Radiodiagnostic
Agent for Intravenous Injection.
Rx ONLY
Iobenguane Sulfate I 123 10 mCi
(370 MBq) in 5 mL solution at calibration.
Expires 36 hours after calibration time.
Each mL of solution contains 0.08 mg
iobenguane sulfate, 23 mg sodium
dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, 2.8 mg
disodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate,
1% benzyl alcohol with a pH of 5.0 - 6.5.
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F).
See package insert for dosage and
administration.
NDC 17156-235-01
CAUTION
RADIOACTIVE
MATERIAL
GE Healthcare
Medi-Physics, Inc.
Arl. Hgts, IL 60004
800-654-0118
Product No. 2035
Est. Lic. No. 100129-A
41-2035

| ADREVIEW
iobenguane i-123 injection |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Labeler - Medi-Physics Inc. (095263729) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
| Medi-Physics Inc. | 095263729 | MANUFACTURE(17156-235), RELABEL(17156-235), REPACK(17156-235), ANALYSIS(17156-235) | |